中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (25): 3778-3784.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.25.020
• 细胞外基质材料 extracellular matrix materials • 上一篇 下一篇
基于气动控制三维打印蔗糖支架的工艺参数
赵小波,孙开渝,刘 翀
- 杭州电子科技大学,生物医学工程与仪器研究所,浙江省杭州市 310018
Three-dimensional printing of a sucrose scaffold based on pneumatic control: relevant technological parameters
Zhao Xiao-bo, Sun Kai-yu, Liu Chong
- Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Instrument, Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
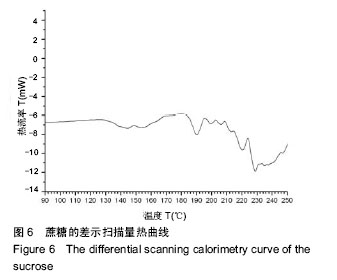
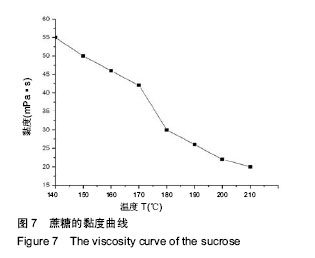
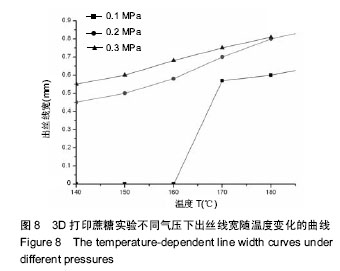
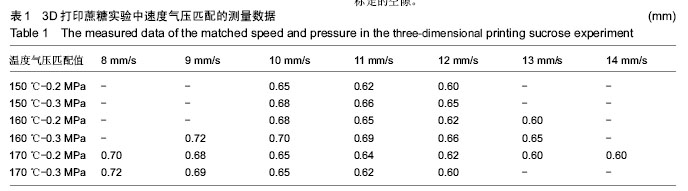
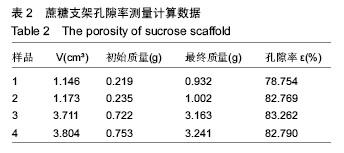
摘要 背景:蔗糖材料是较为理想的辅助支撑和填充模具材料,很适合在3D打印医疗领域推广应用,目前国内外已有了很多将蔗糖作为打印材料的研究,但制备的支架在精度和孔隙率方面还存在一定的问题。 目的:通过3D打印技术研究蔗糖支架的工艺参数。 方法:从物理和化学性质出发,研究蔗糖黏度和热分解随温度的变化情况,基于气动控制的FDM技术,通过研究成型过程中的温度气压匹配、分层设定、速度气压匹配等工艺参数,得到良好成型的蔗糖支架,并对其进行显微镜观察标定,采用液体浸泡法(无水乙醇)测定支架的孔隙率。 结果与结论:蔗糖材料在温度达到180 ℃就会发生完全熔融,流动性最大,超过195 ℃就会发生焦糖反应;它的黏度随着温度的升高而变小。基于气动控制的三维打印机对蔗糖支架进行成型的最佳工艺参数为170 ℃-0.2 MPa-12 mm/s(温度-气压-打印速度)。对于良好成型的蔗糖支架,其线宽达到了700 μm,平均孔隙率达到了81.893%。
中图分类号:
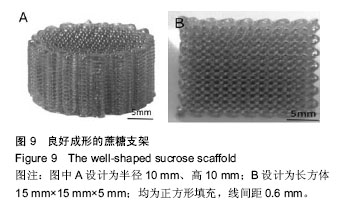
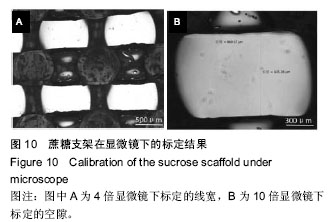
.jpg) 蔗糖材料,由于极易溶于水且廉价易得、环保无污染,很早就被应用于3D打印领域[11],是较为理想的辅助支撑和填充模具材料,很适合在3D打印医疗领域推广应用[2-13]。目前国内外已有了很多将蔗糖作为打印材料的研究,如:西安交通大学的Chen等利用FDM技术,以蔗糖为原料,制备出了人工骨支架;美国麻省理工学院的研究人员利用蔗糖实现了对肝脏的快速成型。但上述研究只是利用蔗糖材料重建了规则的单元模型,而且由于技术和条件的限制,其制备的支架在精度和孔隙率方面还存在一定的问题。
蔗糖材料,由于极易溶于水且廉价易得、环保无污染,很早就被应用于3D打印领域[11],是较为理想的辅助支撑和填充模具材料,很适合在3D打印医疗领域推广应用[2-13]。目前国内外已有了很多将蔗糖作为打印材料的研究,如:西安交通大学的Chen等利用FDM技术,以蔗糖为原料,制备出了人工骨支架;美国麻省理工学院的研究人员利用蔗糖实现了对肝脏的快速成型。但上述研究只是利用蔗糖材料重建了规则的单元模型,而且由于技术和条件的限制,其制备的支架在精度和孔隙率方面还存在一定的问题。
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
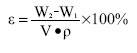
.jpg)